What is Service-oriented Architecture in NodeJS?
Service-oriented architecture is a way to build backend applications consisting of multiple independent services. A service can be any business logic that completes an action and provides a specified result to the endpoint user.
Each service in SOA is a complete business function in itself.
For an Example
Let’s discuss this at a grocery store.
The owner adds the product details to the inventory. The owner searches to find data about a unique product. And the backend application database query should be inside the service section by leveraging the data access layer. Then it securely fetches data and gives the response to the owner.
Layers in Service-oriented Architecture
- Router layer
- Service layer
- Data access layer
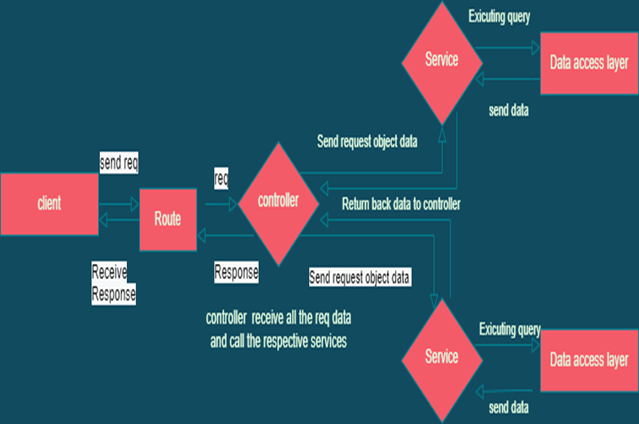
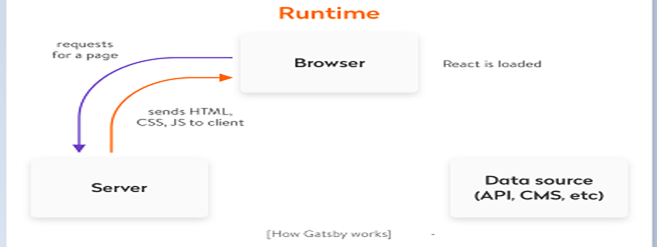
How SOA Works
- Here first when the API call, in the node app first it faces the router section where all the authentication and validation occur through the middleware function. Then control moves toward the controller section which work is collect the incoming data related to API requests. Here all the business logic to access data is combined inside a service. So the controller invokes that service and service leverage data access layer to connect with database and calculation. Then services return the data to the controller. After that controller gives the response to the endpoint user.
- The most important benefit of SOA is as all the services are independent and small chunks so whenever we want to change our programing language it should be very fast and easy in the development process.
Flow chart diagram:
SOA Advantages
- Reliable– Even though service-oriented architecture has small and independent services, it becomes easier to debug code as it checks small chunks instead of checking a large codebase
- Independent of location– Services can be accessed through URL therefore change in location doesn’t affect customer experience
- Scalable– Service-oriented architecture can run on multiple platforms and can operate various servers within the given environment
- Reusability– The SOA uses its services in multiple applications independently without disturbing other services
- Easy maintenance– SOA is an independent unit therefore updating becomes easy as it is a single entity
- Agile– Due to reusable components and services, it helps developers to integrate and build applications quickly according to requirements and consequently increases the agility of service-oriented architecture.
Now the question is why we shouldn’t do this directly inside the controller.
As the router is built with express so it is combined with req and res objects. So when we put our business logic inside the controller then at the testing we have to write a mock for the test with a response mock.
The problem is when we try to only test our business logic we can’t do that but when we combined that inside service we can test that service without req, res object.
Code Example:
In this example, we create a service that resists a user in the database for sign-up API.
In user.js controller receive all the requested data and call the user service
[code language=”css”]
// controllers/user.js
const UserService = require( "../services/UserService" );
const UserServicesec = new UserService();
async function makeUser ( req, res ) {
try {
let bodyData = req.body;
const makeUser = await UserServicesec.create( bodyData );
return res.send( makeUser );
} catch ( err ) {
res.
status( 500 ).
send( err );
}
}
module.exports = { makeUser };
[/code]
Then in the user service folder import the data access layer and database model then service used that data access layer and executes the query in the database
[code language=”css”]
// services/UserService.js
// Data Access Layer
const MongooseService = require( "./MongooseService" );
const userModel = require( "../models/user" );
class UserService {
constructor () {
this.MongooseService = new MongooseService( userModel );
}
async create ( createUser ) {
try {
const result = await this.MongooseService.create( createUser );
return { success: true, body: result };
} catch ( err ) {
return { success: false, error: err };
}
}
}
module.exports = UserService;
[/code]
Conclusion:
The main aim of service-oriented architecture is to allow users to mix large chunks of functionalities into one in order to build an application and services by combining services. This architectural design of node backend application is considered a best practice in industrial labels.