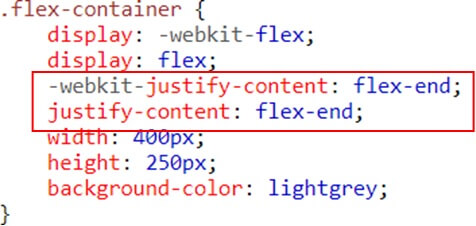
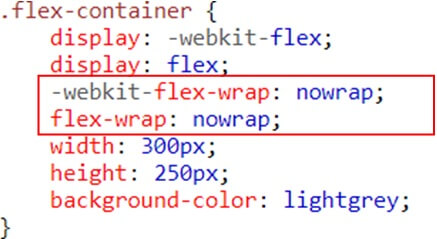
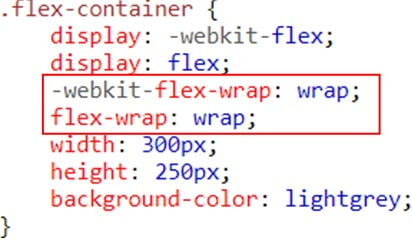
SASS (Syntactically awesome style sheets) is an extension of the CSS which adds syntactic power to the basic CSS language making it easier for developers to write CSS. It is just a CSS preprocessor so that you can write CSS in an easy and convenient way.
“Sass is a meta-language on top of CSS that’s used to describe the style of a document cleanly and structurally, with more power than flat CSS allows. Sass both provides a simpler, more elegant syntax for CSS and implements various features that are useful for creating manageable style sheets.”
“Sass is an extension of CSS3, adding nested rules, Variables, mixins, selector inheritance, and more. It’s translated to well-formatted, standard CSS using the command line tool or a web-framework plugin.”
It’s Sass, not SASS. Sass doesn’t stand for anything, except maybe making your CSS Sassier. Sass makes CSS sassier because it’s a preprocessor. Preprocessors make writing code easier.
If it helps you make CSS more like a real programming language. If that doesn’t help, just think of it as a way to write CSS that’s cleverer.
The History of SASS:
- Sass was first given life by Hampton Catlin in 2006, later supported by Natalie Weizenbaum and Chris Epstein
- Sass started life in the ruby community
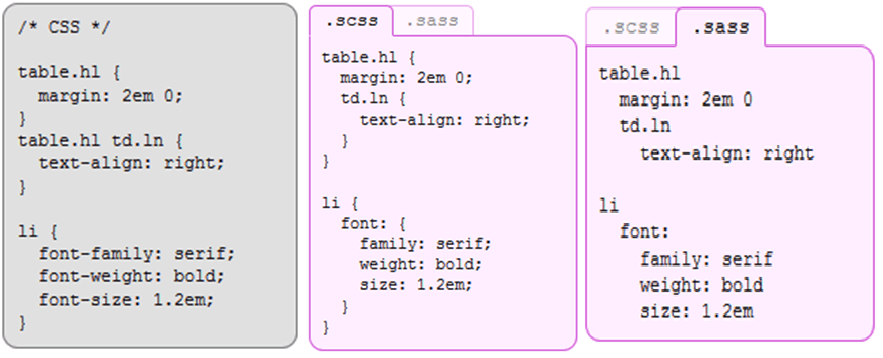
- Sass supports two syntaxes
–Indentation syntax with file ext .sass
–CSS compatible syntax with file ext .scss
- Sass is free to use and requires no license.
Why Use SASS?
- Modularize (@import)
- Variables for maintainability
- Mixins improve reusability
- Reduces redundant rules (keep it DRY)
- Scalable and Maintainable
- Sass is completely compatible with all versions of CSS
- Sass reduces the repetition of CSS and therefore saves time
- It provides the document style in a good, structured format, better than vanilla CSS
- It uses re-usable methods, logic statements, and some of the built-in functions such as color manipulation, mathematics, and parameter lists
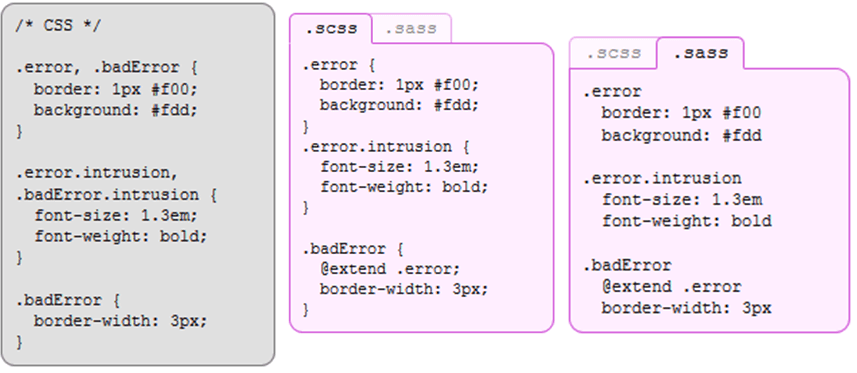
SASS and SCSS
Two available syntaxes
SASS
- HAML-style indentation
- No brackets or semi-colons, based on indentation
- Fewer characters to type
- Enforced conventions/neatness
SCSS
- Semi-colon and bracket syntax
- Superset of normal CSS
- Normal CSS is also valid SCSS
- Newer and recommended
How to Install SASS on Computer
Install Live SASS Compiler Extension in VS Code
- Select the Extensions tab from the sidebar. Click on the Extensions tab from the sidebar
- Search for Live Server in the search box
- Search for “Live Sass Compiler” from the search box
- Click on the Install button
- It is now in the NodeJS package also
- First, install NodeJS
- then Enter NPM install –g sass
The SASS File structure pattern
[code language=”css”]
sass/
|
|– abstracts/ (or utilities/)
| |– _variables.scss // Sass Variables
| |– _functions.scss // Sass Functions
| |– _mixins.scss // Sass Mixins
|
|– base/
| |– _reset.scss // Reset/normalize
| |– _typography.scss // Typography rules
|
|– components/ (or modules/)
| |– _buttons.scss // Buttons
| |– _carousel.scss // Carousel
| |– _slider.scss // Slider
|
|– layout/
| |– _navigation.scss // Navigation
| |– _grid.scss // Grid system
| |– _header.scss // Header
| |– _footer.scss // Footer
| |– _sidebar.scss // Sidebar
| |– _forms.scss // Forms
|
|– pages/
| |– _home.scss // Home specific styles
| |– _about.scss // About specific styles
| |– _contact.scss // Contact specific styles
|
|– themes/
| |– _theme.scss // Default theme
| |– _admin.scss // Admin theme
|
|– vendors/
| |– _bootstrap.scss // Bootstrap
| |– _jquery-ui.scss // jQuery UI
|
`– main.scss // Main Sass file
[/code]
[code language=”css”]
@import ‘abstracts/variables’;
@import ‘abstracts/functions’;
@import ‘abstracts/mixins’;
@import ‘vendors/bootstrap’;
@import ‘vendors/jquery-ui’;
@import ‘base/reset’;
@import ‘base/typography’;
@import ‘layout/navigation’;
@import ‘layout/grid’;
@import ‘layout/header’;
@import ‘layout/footer’;
@import ‘layout/sidebar’;
@import ‘layout/forms’;
@import ‘components/buttons’;
@import ‘components/carousel’;
@import ‘components/slider’;
@import ‘pages/home’;
@import ‘pages/about’;
@import ‘pages/contact’;
@import ‘themes/theme’;
@import ‘themes/admin’;
[/code]
Reasons We Love SASS
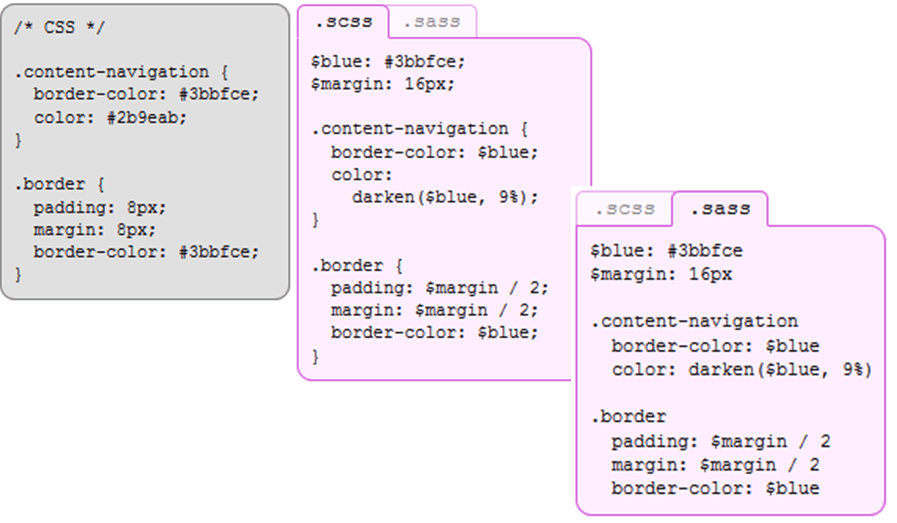
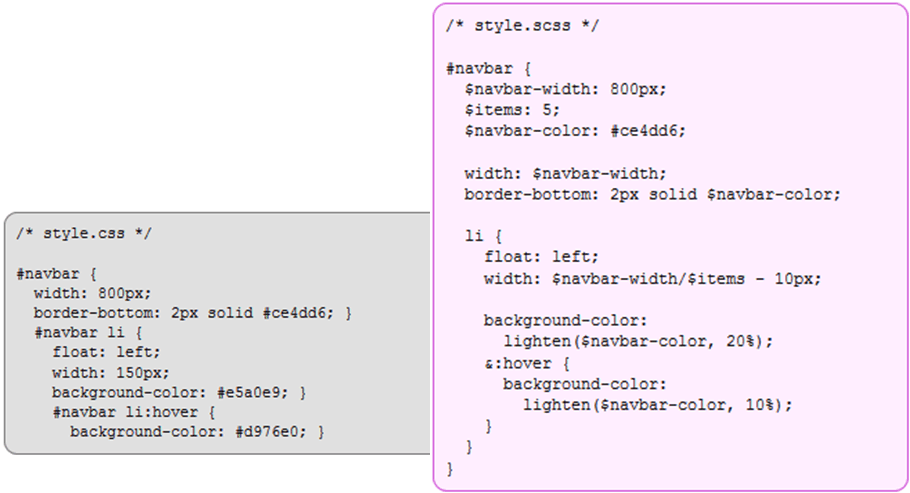
1. Variables
- Sass allows declaring variables that can be used throughout the style sheet
- Variables begin with $ and are declared like properties
- They can have any value that’s allowed for a CSS property, such as colors, numbers, or text
Variables: SASS vs. SCSS
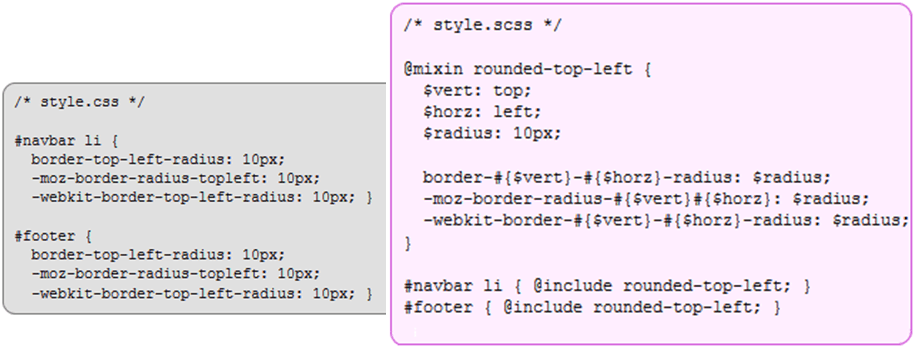
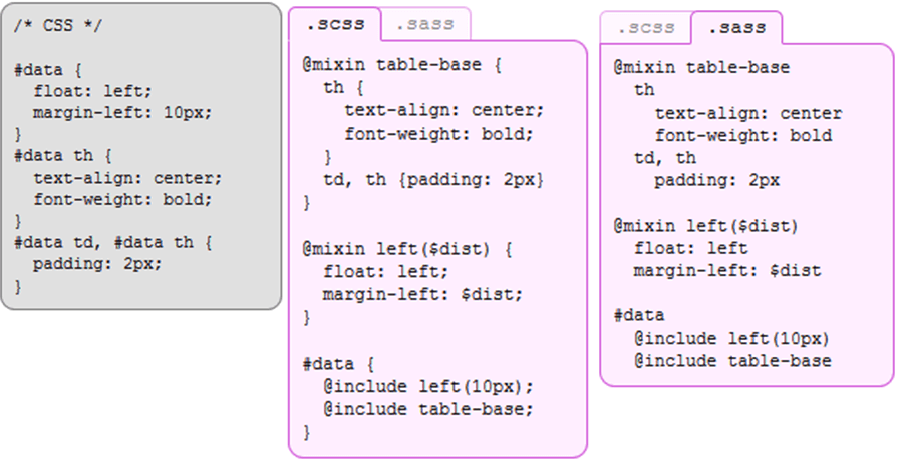
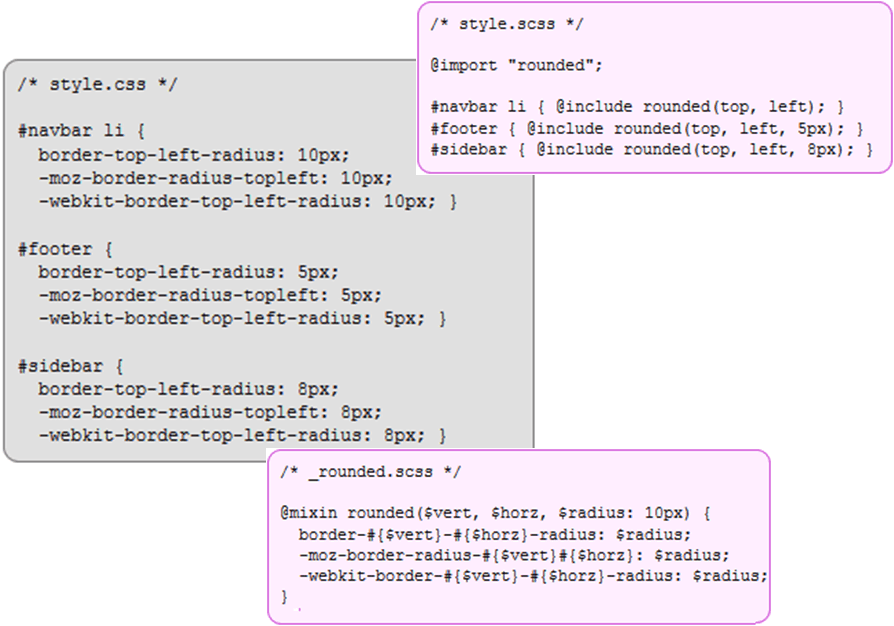
2. Mixins
Mixins allow re-using whole chunks of CSS, properties, or selectors
Mixins are defined using the “@mixin” directive, which takes a block of styles that can then be included in another selector using the “@include” directive
Mixins: SASS vs. SCSS
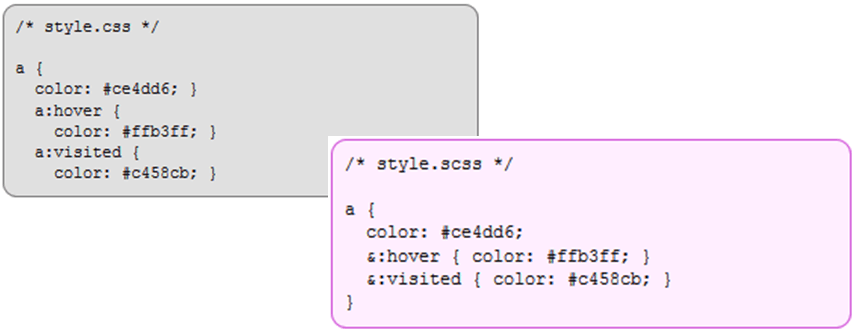
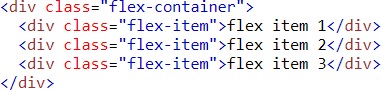
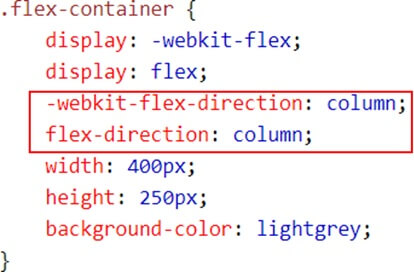
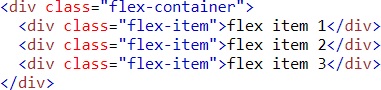
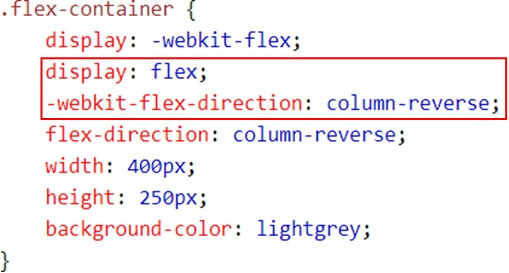
3. Nesting
- Often in CSS, there are several selectors that begin in the same way
- Sass avoids repetition by nesting selectors within one another
Properties can be nested too
- Pseudo-classes can be nested too (e.g.:hover)
- Sass special character & in a selector & is replaced with the parent selector
Nesting: SASS vs. SCSS
4. Imports
Style sheets can be big: the @import directive allows to break styles up into multiple style sheets
5. Operator and functions
- Sass supports basic math operations and many useful functions
- The standard math
- Operations (+, -, *, /, and %) are supported for numbers
There are many useful functions for colors, e.g. To change lightness, hue, saturation,
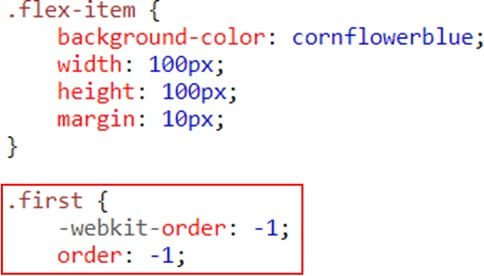
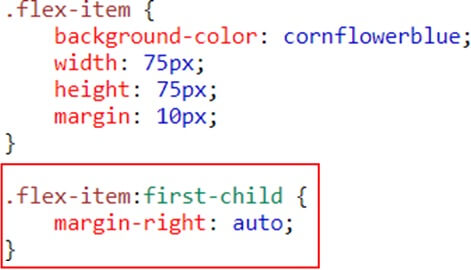
6. Selector Inheritance
Sass can tell one selector to inherit all the styles of another without duplicating the CSS properties
Conclusion:
Organizing code is essential for developers and together with all other skills. It is the most effective way to improve the functioning of the site. And even though there are multiple ways of organization and different strategies, opting for simplicity helps you avoid dangerous pitfalls. And finally, there is no right or wrong choice since everything depends on the developer’s work strategies.