RESTful APIs have become the backbone of modern web applications, enabling seamless communication between different systems. In this comprehensive guide, we will walk through each step of creating RESTful APIs using the Laravel framework.
We will explore best practices, provide code examples, and cover essential concepts to ensure you’re equipped to build robust and efficient APIs.
Why RESTful API?
RESTful APIs, short for Representational State Transfer, is an architectural style that defines a set of constraints for designing networked applications.
It emphasizes simplicity, scalability, and statelessness, making it an ideal choice for building APIs.
use standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to perform CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on resources.
Why Choose Laravel?
Laravel, a PHP web application framework, offers a wide range of tools and features that streamline API development.
It provides an expressive syntax, a robust ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) called Eloquent, and built-in support for routing, authentication, and database operations.
Laravel’s combination of power and simplicity makes it an excellent choice for building RESTful APIs.
Setting Up a Laravel Project
Before diving into API development, ensure you have a solid Laravel project environment in place. Follow these steps:
-
Install Laravel:
Start by installing Laravel using Composer, a PHP dependency manager. Open your terminal and run the following command:
composer create-project –prefer-dist laravel/laravel project-name
Replace “project-name” with your desired project name.
-
Configure Environment:
Set up your database connection in the ‘.env’ file. Configure other project settings such as timezone and application name in the same file.
-
Generate Key:
Generate an application key by running:
php artisan key:generate
-
Clear Cache:
Clear the cache using the following command to ensure that your application operates smoothly:
php artisan config:cache
php artisan config:clear
-
Add New Library into Laravel Application
If you need to include new libraries or packages, you can do so using Composer.
composer require barryvdh/laravel-dompdf
-
Storage Link:
To create a symbolic link from the public directory to the storage directory, use the following command:
php artisan storage:link
-
Run Application:
To ensure everything is working correctly, run a local development server:
php artisan serve
Visit http://localhost:8000 in your browser to see the Laravel welcome page.
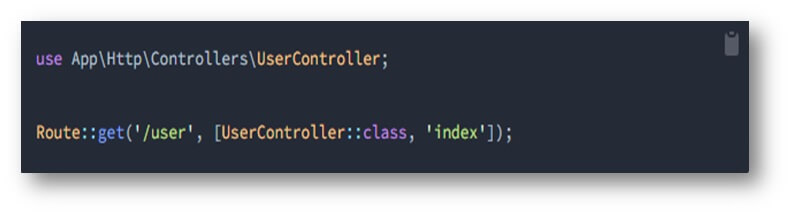
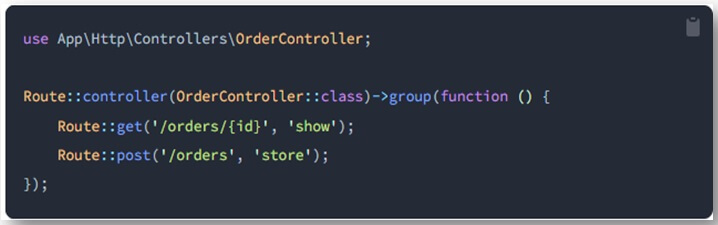
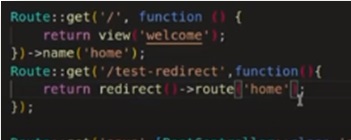
Defining Routes and Controllers
In Laravel, routes define the entry points to your application, and controllers handle the logic for those routes. For API development, create routes and controllers as follows:
-
Create a Controller:
Generate a controller using Artisan:
php artisan make:controller ApiController
This command creates a new controller named ApiController.
-
Define Routes:
Open the routes/api.php file and define your API routes using the Route facade. For example:
Route::get(‘/posts’, ‘ApiController@getPosts’);
Route::post(‘/posts’, ‘ApiController@storePost’);
This code defines routes for retrieving and creating posts.
-
Implement Controller Methods:
In the ApiController created earlier, implement methods like getPosts and storePost to handle the corresponding routes’ logic.
public function getPosts()
{
// Retrieve and return posts
}
public function storePost(Request $request)
{
// Validate and store a new post
}
Your routes and controllers are now set up to handle API requests.
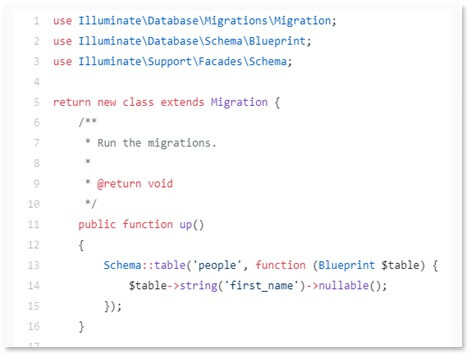
Migration & Seeders
-
Creating a Migration:
php artisan make:migration create_posts_table
-
Running Migrations:
php artisan migrate
-
Rollback Migrations:
php artisan migrate:rollback
-
Creating a New Migration for Modifying Tables:
php artisan make:migration add_author_to_posts
-
Running Seeders:
php artisan db:seed
-
Rollback and Refresh Database:
php artisan migrate:refresh
Handling Request and Response Formats
APIs often communicate in JSON format. Laravel makes it easy to handle JSON requests and responses:
-
Parsing JSON Requests:
To parse JSON data from incoming requests, add the json() middleware to your API routes:
Route::post(‘/posts’, ‘ApiController@storePost’)->middleware(‘json’);
This middleware will automatically parse the JSON request data into a PHP array.
-
Returning JSON Responses:
To return JSON responses, you can use Laravel’s response() method:
public function getPosts()
{
$posts = // Retrieve posts
return response()->json($posts);
}
This ensures your API communicates in the desired format.
Authentication and Authorization
Securing your API is crucial. Laravel offers robust solutions for authentication and authorization:
-
Authentication:
Laravel provides built-in authentication scaffolding using php artisan make:auth. You can also use Passport, a Laravel package, to implement OAuth2 authentication.
-
Authorization:
Define authorization policies and gates to control access to resources. For example, you can create a policy to check if a user is authorized to update a post.
public function update(User $user, Post $post)
{
return $user->id === $post->user_id;
}
Implement middleware to protect routes:
Route::put(‘/posts/{post}’, ‘ApiController@updatePost’)->middleware(‘can:update,post’);
-
Token-Based Authentication:
For token-based authentication, use Laravel Passport. It allows clients to authenticate using API tokens, making it suitable for mobile and third-party applications.
Validation and Error Handling
-
Request Validation:
Laravel’s request validation simplifies input validation. Define validation rules in your controller methods:
public function storePost(Request $request)
{
$validatedData = $request->validate([
‘title’ => ‘required|max:255’,
‘body’ => ‘required’,
]);
// Store the post
}
-
Error Handling:
Leverage Laravel’s error handling capabilities. Customize error responses by modifying the render method in the app/Exceptions/Handler.php file.
public function render($request, Throwable $exception)
{
if ($exception instanceof ModelNotFoundException) {
return response()->json([‘error’ => ‘Resource not found’], 404);
}
return parent::render($request, $exception);
}
Customize error messages and responses to provide clear feedback to API consumers.
Implementing CRUD Operations
-
Create, Read, Update, Delete (CRUD):
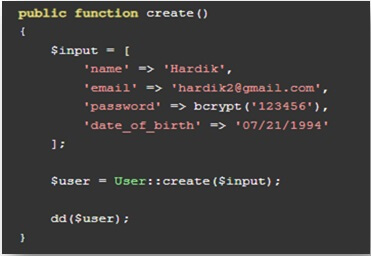
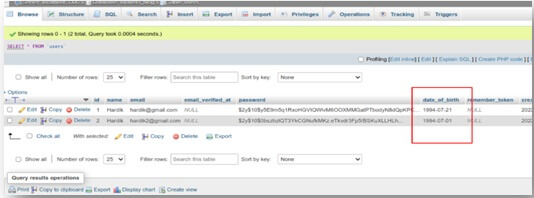
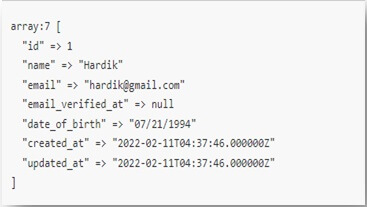
Implement CRUD operations in your controller methods. Laravel’s Eloquent ORM simplifies database interactions:
public function storePost(Request $request)
{
$post = new Post();
$post->title = $request->input(‘title’);
$post->body = $request->input(‘body’);
$post->save();
// Create a new post
}
// Implement methods for reading, updating, and deleting posts.
Eloquent provides a fluent and expressive way to work with your database tables.
Pagination and Sorting
To handle large datasets, implement pagination and sorting:
-
Pagination:
Use Laravel’s paginate method to split query results into pages:
$posts = Post::paginate(10);
This code retrieves 10 posts per page.
-
Sorting:
Allow clients to sort data using query parameters:
$orderBy = request()->query(‘orderBy’, ‘created_at’);
$direction = request()->query(‘direction’, ‘asc’);
$posts = Post::orderBy($orderBy, $direction)->paginate(10);
This enables users to specify sorting criteria in API requests.
Versioning Your API
APIs evolve over time, and versioning helps ensure backward compatibility:
-
URL Versioning:
Prefix API routes with a version number:
Route::prefix(‘v1’)->group(function () {
Route::get(‘/posts’, ‘ApiController@getPosts’);
// Other routes
});
This allows you to make breaking changes while maintaining older versions.
-
Accept Header Versioning:
An alternative approach is using the Accept header in requests to specify the API version. Implement middleware to handle this:
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
$request->headers->set(‘Accept’, ‘application/vnd.myapi.v1+json’);
return $next($request);
}
This method offers flexibility for clients to choose the API version.
Testing Your API
Testing is crucial to ensure your API works as expected. Laravel provides a testing suite:
-
PHPUnit Tests:
Write PHPUnit tests for your API routes and controllers. Laravel’s TestCase class offers useful methods for simulating HTTP requests.
public function testGetPosts()
{
$response = $this->get(‘/api/posts’);
$response->assertStatus(200);
// Add more assertions
}
-
Testing Authentication:
Test authentication flows, ensuring that protected routes reject unauthenticated requests.
public function testAuthenticatedRoute()
{
$user = factory(User::class)->create();
$response = $this->actingAs($user)->get(‘/api/protected-route’);
$response->assertStatus(200);
// Add more assertions
}
Testing ensures that your API remains reliable during development and updates.
Performance Optimization
-
Caching:
Use Laravel’s caching system to store frequently requested data. Cache responses to reduce database queries.
$posts = Cache::remember(‘posts’, 60, function () {
return Post::paginate(10);
});
This code caches the posts for 60 seconds.
-
Database Indexing:
Create appropriate database indexes for frequently queried columns to speed up database operations.
-
Query Optimization:
Review and optimize database queries for better performance. Use Laravel’s query builder and Eloquent optimizations.
Security Considerations
-
Input Sanitization:
Sanitize input data to prevent SQL injection and other security vulnerabilities.
$cleanInput = filter_var($request->input(‘input’), FILTER_SANITIZE_STRING);
-
Rate Limiting:
Implement rate limiting to protect your API from abuse and ensure fair usage.
-
Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS):
Configure CORS settings to control which domains can access your API.
-
Data Validation:
Always validate user input to prevent invalid data from reaching your application.
Deployment and Scaling
-
Deployment:
Deploy your Laravel API to a production server. Common choices include shared hosting, virtual private servers (VPS), and cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Heroku.
-
Scalability:
Plan for scalability by using load balancers, caching layers, and database replication. Consider horizontal scaling with multiple application servers.
-
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD):
Implement CI/CD pipelines to automate the deployment process and ensure smooth updates.
Real-World Example: Building a Task Management API
To tie everything together, let’s build a real-world example: a Task Management API. This API will allow users to create, read, update, and delete tasks, with authentication and validation in place.
- Define routes and controllers for tasks.
- Implement authentication with Laravel Passport.
- Set up request validation and error handling.
- Implement CRUD operations for tasks.
- Add pagination and sorting.
- Test the API thoroughly.
- Optimize performance and address security concerns.
By following these steps and best practices, you’ll have a robust and secure RESTful API built with Laravel, ready to power your web or mobile applications.
FAQs
What is Laravel and why is it popular in web development?
Laravel is a PHP web application framework known for its elegant syntax, developer-friendly features, and robust ecosystem.
Are you looking for a Laravel developer
It’s popular because it simplifies common web development tasks, offers powerful tools for routing, authentication, and database management, and encourages best practices, making it an ideal choice for building modern web applications.
What are the key features of Laravel that make it stand out among other PHP frameworks?
Laravel offers several standout features, including its elegant ORM (Eloquent), a powerful templating engine (Blade), built-in authentication and authorization, a robust ecosystem of packages (Composer), and a convenient command-line tool (Artisan) for automating tasks and generating code, which collectively enhance developer productivity and code quality.
How does Laravel handle security concerns in web development?
Laravel prioritizes security with built-in features such as protection against SQL injection, cross-site request forgery (CSRF), and cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks.
It also offers an authentication system that includes user password hashing, session management, and role-based access control, all designed to secure web applications effectively.
What is Laravel’s role in API development, and why is it a popular choice for building RESTful APIs?
Laravel provides a seamless platform for creating RESTful APIs. Its routing system and resource controllers simplify API endpoint creation, while features like middleware, request validation, and API token handling ensure robust security. The Laravel Passport package also streamlines API authentication.
How can developers get started with Laravel, and what resources are available for learning and mastering this framework?
Developers can start with Laravel by visiting the official Laravel website (laravel.com) and following the documentation and tutorials available there.
Additionally, there are numerous online courses, forums, and community-contributed packages that provide extensive resources for learning and mastering Laravel, making it accessible for developers at all levels of expertise.
Conclusion:
Building RESTful APIs with Laravel is a powerful and efficient way to enable communication between your applications and external systems.
By following the steps outlined in this guide and adhering to best practices, you can create a scalable, secure, and reliable API that meets the needs of your projects and users. Happy coding!