Python, an open-source programming language, is widely utilized in various domains such as data science, machine learning, web development, application development, Fintech, and more.
Python application development in particular, is highly sought-after for the creation of web and mobile apps.
According to StackOverflow, Python is the fastest-growing programming language and the top choice among developers.
In fact, nearly 2% of all websites on the internet utilize Python as their server-side programming language.
Python was initially developed by Guido Van Rossum in the late 80s, and since then, its popularity has continued to soar.
If you’re interested in Python, understanding its usage in web and mobile technologies is crucial.
What is Python?
Python is a versatile general-purpose programming language that goes beyond web development. Unlike HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, Python can be used for other types of software development as well.
Python finds its application in various areas, including:
- Server-side web and mobile app development
- Desktop app and software development
- Processing big data and other mathematical calculation
- Writing system scripts
Python is highly sought after for two main reasons: its ability to handle a wide range of tasks and its beginner-friendly nature.
Python boasts a simple syntax that makes it accessible to anyone looking to learn and get started with programming.
Python application development included but not limited to web app development, mobile app development, data science, machine learning, artificial intelligence, wearable OS development, business intelligence and more.
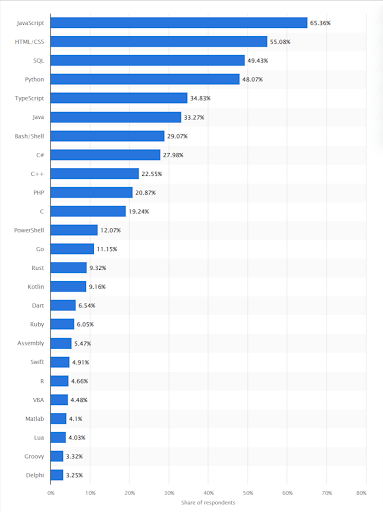
Top 7 Python Programming Language Usage
(Source: statista.com)
-
Application of Python in Data Science
Today’s most talked about usage in Python is in data science. It is a process of extracting information and insights from data which includes Machine Learning, Data Visualization and Data Analysis.
Never miss an update from us. Join 10,000+ marketers and leaders.
Machine Learning is the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) where machines are programmed to learn without having to program what to do. It enables computers to program themselves.
A good example of ML algorithms include the video suggestions and recommendations you get from applications such as YouTube and NetFlix.
-
Why Python for machine learning and artificial intelligence
Since the inception of Python it has been used for scientific and numerical computing. Moreover, because ML is basically numerical computing, Python is extremely useful for ML.
With the introduction of technologies and frameworks like Tensorflow by Google, Python has become the de-facto language for ML applications. Pytorch – another deep learning platform started by Facebook has also gained popularity.
Python comes bundled with scikit-learn which is a simple and easy-to-use ML package enabling developers to get started on Machine Learning pretty easily.
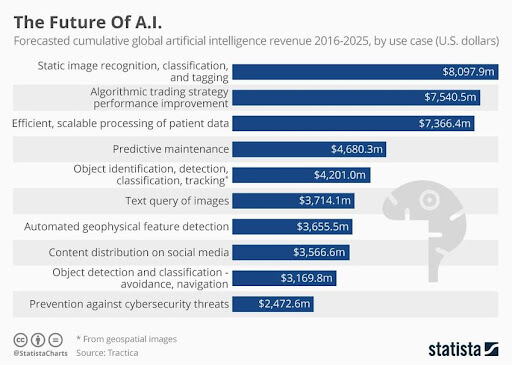
Additionally, Python comes with scikit-learn, a simple and easy to use ML package that can get you started very easily in Machine Learning. You can see the increase of popularity in these ML platforms in the graph below.
3. Python for Data Visualization
Python is widely used for data visualization and data analysis. With the exponential growth of data generated on the internet (2.5 quintillion bytes daily), data analysis becomes crucial for businesses to effectively harness this vast amount of information.
Data visualization plays a vital role in helping companies make sense of large datasets.
By visually representing data, businesses and researchers can identify patterns and forecast the future impact of those patterns.
Rather than presenting raw numbers on a table, visualizations make data more meaningful and impactful.
Libraries such as matplotlib and seaborn simplify the process of creating bar graphs, distribution maps, and heat maps, allowing users to derive valuable insights with just a few lines of code.
4. Python for web development
Web development includes activities such as creating websites and web-based software applications.
It consists of two main components: the client-side, which runs code on the browser, and the server-side, which processes logic and interacts with databases and other servers.
While JavaScript is a popular choice for client-side development, Python shines on the server-side.
Python web frameworks like Django and Flask enable efficient development of dynamic web applications without the need to learn a client-side language like JavaScript.
Python web frameworks, such as Django Rest Framework, significantly reduce development time by automating common web development tasks. Its ease of use makes it a preferred choice among tech enthusiasts.
5. Python for Application Development
Python offers several advantages for application development, including reduced development time and effort.
It is ideal for prototyping due to its robustness, scalability, speed, and versatility, making it suitable for both small-scale and enterprise-level projects.
According to a research by iDataLabs – 69% of companies that use Python are small (<$50M in revenue), 9% are medium-sized ($50M – $1000M in revenue) and 16% are large (>$1000M in revenue).
Python provides a database API that simplifies connections to databases like MySQL, Oracle, and PostgreSQL.
Its ability to interface with languages such as C and Java allows developers to leverage functionality from other programming languages in Python applications.
Python is often likened to building blocks that can be combined to create new applications. By carefully selecting and integrating these blocks or modules, developers can create applications more efficiently.
Additionally, Python’s open-source nature enables developers to contribute new packages to solve problems and share them with the community.
6. Python for automation scripts
Python excels in scripting, allowing developers to write small programs that perform multiple tasks automatically.
It is ideal for such purposes as it emphasizes quick and easy coding. Web scraping, for instance, is a popular use case of Python scripting.
It involves parsing websites and extracting relevant data, which can then be stored in formats like CSV for further analysis using machine learning algorithms.
7. Python in Fintech
Financial technology or Fintech, is a technology that automates and improves the delivery of financial services.
This includes online banking, stock market trading, online transactions, and bitcoin transactions using blockchain applications.
Fintech is utilized in various finance-related sectors such as investment, portfolio management, banking, education, and fundraising.
According to a survey by HackerRank – Python is among the top three most popular languages used in financial services companies and one of the top languages in FinTech.
Python’s ease of use and modular nature makes it the perfect programming language for Fintech.
It is also an ideal choice of programming language for fintech because it can be employed for machine learning and data science libraries and capabilities.
For example, using machine learning to automatically detect fraud through payment history can save companies millions of dollars.
That’s why top financial institutions like Stripe, Revolut, and Robinhood incorporate Python in their software development.
Furthermore, Python finds application not only in Fintech but also in other industries such as game development, GUI application development, networking, testing, robotics, and embedded applications.
Advantages of Python Programming Language
-
Easy to Learn and Write:
Python is a high-level programming language with a syntax that resembles natural language. This makes Python easier to read and understand, requiring fewer lines of code compared to other languages like C/C++ and Java.
-
Improved Productivity:
The simplicity of Python allows developers to focus more on problem-solving rather than spending time understanding complex syntax. This leads to writing less code and achieving higher productivity, as well as faster debugging.
-
Interpreted Language:
Python is an interpreted language, executing the code line by line. It stops execution and reports errors if any are encountered. Debugging becomes easier as Python provides feedback on the first encountered error, even if multiple errors exist.
-
Typed Dynamically:
Python doesn’t know the type of variable until the code is run. It automatically assigns the data type during execution. Python application developers don’t need to worry about declaring variables and their data types.
-
Free and Open-Source:
Python is free to use and distribute due to its open-source license. Users can modify the source code and distribute their own versions of the Python programming language.
-
Vast Libraries:
The Python library is huge where you can find almost all the functions you need to perform coding tasks. Python application developers don’t have to depend on external libraries.
If you intend to use an external library you can use Python package manager (pip) which makes it easier to import other packages from Python package index (PyPi) which consists of over 2 million packages.
-
Portability:
In other languages such as C and C++, you need to change the code each time you run on different platforms but with Python you can write it once and run it anywhere.
Disadvantages of Python Programming Language
-
Slower Speed:
As mentioned above, Python’s nature as an interpreted language means that it executes each line of code sequentially, resulting in slower execution.
The dynamic nature of Python is also responsible for the slow speed of Python because it has to do extra work while executing the code.
-
Python is not Memory Efficient:
Python’s usage of memory for storage and execution is significantly higher than that of other programming languages, which renders it unsuitable for constructing applications that require memory optimization.
-
Inefficient Mobile Computing:
Python is typically used in server-side programming. Because Python is not memory efficient and has a slow processing power it is not the most suitable application development technology for mobile app development.
-
Database Access:
Python application development is stress-free but interacting with databases is slower because Python databases are still slower and somewhat outdated compared to other popular technologies.
What Makes Python Suitable for Mobile Application Development?
As mentioned above, developers can use Python to create mobile applications as well. In this section we will explore the possibility of using Python for mobile app development.
Are you looking for a Python developer
Python was not commonly employed for mobile app development because iOS and Android do not support interpreter languages.
But today, with the emergence of several frameworks such as Python GUI frameworks Python can be used to develop apps for Android and iOS devices.
Types of Apps You Can Develop Using Python
-
Audio-Video Apps:
Using Python libraries such as OpenCV and PyDub Python app developers can create music and video-playback and streaming applications for mobile phones.
-
Game App Development:
Using Pygame python app development companies can quickly create game prototypes and test them in real-time. Some of the most popular games such as “Battlefield 2”, “EVE Online” and “World of Tanks” are developed using Python programming language.
-
Blockchain Application:
Since the inception of blockchain it has become one of the most widely used technology trends. It is difficult for developers to create blockchain applications but Python makes it easier.
Python developers use frameworks such as Flask to create endpoints for various features of blockchain.
-
Machine learning apps:
Machine learning is yet another technology that has emerged in the past decade. It is an algorithmic technology which provides data for intelligent decision making. Python offers free libraries such as Pandas and Scikit to develop ML apps with ease.
Wrapping Up!
Python has emerged as a versatile programming language; its ease-of-follow syntax and wide range of applications has made it one of the most sought after programming languages by developers.
Python today has numerous resources and tools which makes python app development even more developer-friendly.
If you are planning to develop mobile apps using Python you can leverage its ease-of-use, diversity and flexibility for various mobile and web app development faster than any other programming languages.
FAQ:
-
Can Python be used for mobile app development?
Yes, Python can be used for mobile app development. Platforms like Kivy, BeeWare, and Pygame enable cross-platform mobile app development. Python’s ease of use and rich library support make it a viable choice for mobile applications.
-
What role does Python play in data-driven applications and machine learning development?
Python plays a crucial role in data-driven applications and machine learning development. Its extensive libraries like Pandas, NumPy, and scikit-learn enable data manipulation, analysis, and building machine learning models, making it a preferred language for data scientists and AI developers.
-
Can Python be used for developing enterprise-level applications with high scalability and performance?
Python is suitable for developing enterprise-level applications with high scalability and performance. Frameworks like Django and Flask provide robust web development capabilities. Python’s asynchronous programming features in libraries like asyncio enhance application performance.
-
Are there any specific industries or sectors where Python is particularly prevalent in application development?
Python’s versatility and ease of use have made it prevalent in various industries and sectors. It is commonly used in web development, scientific research, data analysis, artificial intelligence, finance, and automation, among others.
-
How does Python facilitate rapid prototyping and agile development practices?
Python’s concise syntax and extensive libraries accelerate the development process, making it ideal for rapid prototyping and agile development. Its readable codebase and shorter development cycles allow developers to iterate quickly, adapt to changes, and deliver projects efficiently.