In today’s evolving technological landscape, enterprise businesses are presented with an array of options to streamline their operations and drive growth. One solution that has gained remarkable traction in recent years is Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
This innovative model has transformed the way organizations approach software deployment, offering a wide array of benefits that are particularly well-suited for enterprise-level operations.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the world of SaaS, explore its characteristics, advantages, and dispel common myths, ultimately highlighting why it’s the best option for modern enterprise businesses.
Understanding SaaS:
(Image source: https://www.saasacademy.com/)
It is a cloud computing model in which software applications are hosted and provided to users over the internet on a subscription basis.
Unlike traditional software that needs to be installed and maintained on individual computers or servers, SaaS applications are centrally managed in the cloud, accessible from any device with an internet connection.
This convenience and flexibility have made it a game-changer for businesses of all sizes, but particularly for enterprises with complex needs.
Examples of Popular SaaS Application

(Image source: https://otakoyi.software/)
Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
- Salesforce:
A highly customizable CRM platform that helps businesses manage leads, contacts, opportunities, and customer interactions.
- WakeUpSales:
A user-friendly CRM system that offers contact management, email tracking, and sales automation features.
Project Management and Collaboration:
- Orangescrum:
A project management tool known for its visual task boards and team collaboration features, making it easy to track projects and tasks.
- Monday.com:
A work operating system that provides a centralized platform for planning, tracking, and managing work across teams.
Human Resources Management (HRM):
- Workday:
A cloud-based HRM system that covers HR, payroll, and talent management, designed to streamline workforce management.
- BambooHR:
An HR software that focuses on employee data management, onboarding, and performance tracking.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP):
- Oracle NetSuite:
A comprehensive cloud-based ERP solution that integrates financial management, CRM, and e-commerce functionalities.
- SAP Business ByDesign:
A scalable ERP system that covers various business processes like finance, supply chain, and project management.
Communication and Team Collaboration:
- Microsoft Teams:
A hub for teamwork in Microsoft 365, combining chat, video conferencing, file sharing, and app integration.
- Slack: A messaging and collaboration platform that enhances communication and teamwork with channels, integrations, and file sharing.
Marketing Automation:
- HubSpot Marketing Hub:
An all-in-one marketing automation platform that includes tools for email marketing, social media, and analytics.
- Marketo:
A powerful marketing automation solution that focuses on lead generation, nurturing, and personalized campaigns.
Financial Management:
- QuickBooks Online:
A popular cloud-based accounting software that helps small businesses manage invoicing, expenses, and financial reports.
- Xero:
Another cloud-based accounting platform known for its ease of use and features like bank reconciliation and expense tracking.
E-commerce Platforms:
- Shopify:
A widely-used e-commerce platform that enables businesses to set up online stores, manage products, and process payments.
- WooCommerce:
A plugin for WordPress that turns a website into an e-commerce store, offering customization and integration options.
Customer Support and Helpdesk:
- Zendesk:
A customer service platform that provides ticketing, live chat, and self-service support solutions to enhance customer experience.
- Freshdesk:
A cloud-based helpdesk software that offers omnichannel support, ticket management, and automation features.
Document Collaboration and Storage:
- Google Workspace (formerly G Suite):
A suite of cloud-based productivity tools including Google Docs, Sheets, and Drive for collaboration and storage.
- Microsoft 365 (formerly Office 365):
A collection of applications including Word, Excel, and OneDrive for document collaboration and storage.
Video Conferencing and Communication:
- Zoom:
A widely-used video conferencing platform that offers online meetings, webinars, and collaboration features.
- Microsoft Teams:
Apart from collaboration, it also serves as a platform for video conferencing, making it a versatile choice.
A Brief History of SaaS Applications
The concept dates back to the 1960s, but it gained significant momentum in the 1990s with the advent of the internet.
Salesforce’s launch in 1999 marked a pivotal moment, showcasing the viability of delivering software as a service.
Since then, it has evolved to cover a wide range of applications and industries, disrupting traditional software deployment models.
What are the Characteristics and Benefits of SaaS Applications?
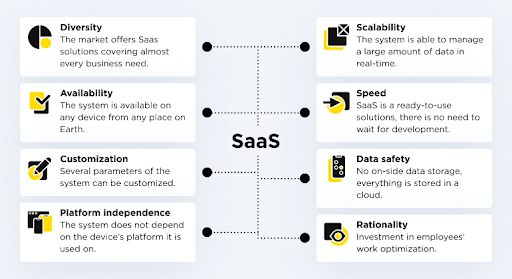 (Image source: https://otakoyi.software/)
(Image source: https://otakoyi.software/)
Scalability and Flexibility:
- Easily Scales:
Applications can scale up or down seamlessly, adapting to changing user demands or business growth without requiring significant infrastructure adjustments.
- No Hardware Upgrades:
Eliminates the need for costly hardware upgrades or expansions, as the cloud infrastructure handles the scaling process.
- Rapid Deployment:
New users or features can be added quickly, allowing businesses to respond to market opportunities or changes without delay.
- Pay-as-You-Grow:
You pay for what you use, making it ideal for startups or enterprises looking to control costs while maintaining the ability to expand operations.
- Resource Efficiency:
It avoids overprovisioning and underutilization of resources, optimizing cost-effectiveness.
Cost-Efficiency and Predictable Pricing:
- Subscription Model:
It operates on a subscription basis, replacing upfront licensing costs with regular, predictable payments.
- Reduced Capital Expenses:
No need for significant upfront investments in software licenses or hardware, freeing up capital for other business priorities.
- Lower Total Cost of Ownership (TCO):
Maintenance, updates, and support are often included in the subscription, reducing the total cost of owning and managing software.
- Scalability Savings:
As your business grows, you avoid the expense of purchasing and maintaining additional hardware and software licenses.
- Budget Predictability:
Fixed subscription fees allow for better budgeting and financial planning, minimizing financial surprises.
Accessibility and Collaboration:
- Anytime, Anywhere Access:
SaaS applications are accessible via the internet, enabling users to work from anywhere and on any device.
- Remote and Hybrid Work:
Supports the rise of remote work, allowing teams to collaborate effectively regardless of geographical locations.
- Real-Time Collaboration:
Multiple users can work simultaneously on shared documents, projects, or data, enhancing teamwork and productivity.
- Reduced Communication Barriers:
Instant messaging, file sharing, and collaborative features facilitate smooth communication and information exchange.
- Global Workforce Enablement:
It breaks down geographic barriers, allowing businesses to tap into talent from around the world.
Automatic Updates and Maintenance:
- Seamless Updates:
Application service providers handle updates and maintenance, ensuring that your software is continuously updated with the latest features and security enhancements.
- Reduced IT Burden:
IT teams are relieved of routine maintenance tasks, allowing them to focus on strategic initiatives and innovation.
- Improved Security:
Regular updates include security patches, reducing vulnerabilities and enhancing protection against cyber threats.
- Minimized Downtime:
Updates are often performed without disrupting users, minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous operation.
- Access to Innovation:
Automatic updates provide access to new functionalities and capabilities without the need for manual installations.
Integration and Interoperability:
- Built-in Integrations:
Many applications offer Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and integrations with other popular software and services.
- Unified Data Flow:
Integrations facilitate data sharing and synchronization across different systems, reducing data silos and improving data accuracy.
- Streamlined Workflows:
Automated data transfer between applications reduces manual data entry and improves efficiency.
- Enhanced Decision-Making:
Unified data and insights from integrated systems enable better-informed decisions across departments.
- Customized Ecosystem:
Organizations can create tailored ecosystems by combining applications that suit their specific needs, ensuring a cohesive software environment.
What is the Difference Between SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) vs. On-Premise Applications
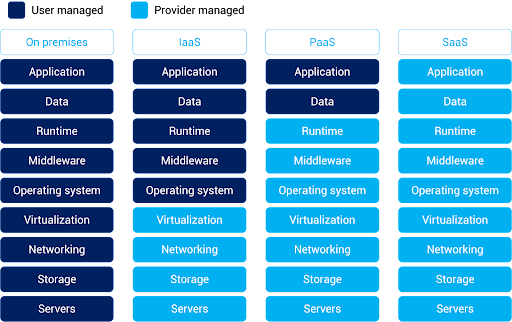
(Image source: https://www.alibabacloud.com/knowledge/what-is-saas)
|
|
SaaS (Software-as-a-Service)
|
On-Premise Application
|
|
Definition
|
SaaS applications are cloud-based software solutions delivered over the internet on a subscription basis. Users access the software remotely through web browsers without needing to install or maintain it locally.
|
On-premise applications are traditional software solutions that are installed and run on local servers or computers within an organization’s physical infrastructure. These applications are managed, maintained, and updated by the organization’s IT department.
|
|
Deployment
|
Deployed on the provider’s servers and accessed remotely via the internet. No installation is required on users’ devices.
|
Installed and maintained on the organization’s own servers, requiring manual installations and updates on each user’s device.
|
|
Cost Structure
|
Follows a subscription-based pricing model, with predictable recurring costs that cover software access, maintenance, updates, and support. |
Involves upfront costs for software licenses and hardware, with potential additional costs for ongoing maintenance, updates, and support. |
|
Accessibility
|
Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering collaboration among distributed teams and enabling remote work.
|
Accessible only within the organization’s network, limiting remote access and collaboration.
|
|
Scalability
|
Scales easily to accommodate increased users, data, or transactions, with the provider managing the underlying infrastructure
|
Requires manual adjustments and potential hardware upgrades to scale, often leading to higher costs and longer implementation times.
|
|
Maintenance and Updates
|
Providers handle maintenance, updates, and security, ensuring that users always have access to the latest features and security patches.
|
Organizations are responsible for maintaining, updating, and patching the software, which can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
|
|
Customization
|
Customization options can be limited, as the software is standardized to cater to a broader user base.
|
Offers greater customization possibilities, allowing organizations to tailor the software to their specific needs.
|
|
Data Security
|
Data security relies on the provider’s measures. Organizations must trust the provider’s security practices and compliance with data protection regulations.
|
Provides more control over data security, but requires organizations to implement and maintain their own security measures.
|
|
Integration
|
Offers built-in APIs and integrations with other software, facilitating seamless data flow across systems.
|
Integrations often require manual development and maintenance, potentially leading to longer integration times.
|
| Vendor Control |
Organizations rely on the SaaS provider for software management, updates, and security, which can lead to concerns about vendor dependency.
|
Organizations have full control over software management, updates, and security, but this also requires dedicated IT resources.
|
Debunking Common Software-As-A-Service Myths
-
Myth: SaaS is Less Secure than On-Premise Software:
Reality: Security is a top priority for providers. Reputable providers invest heavily in advanced security measures, encryption, data backup, and compliance with industry standards. These platforms often offer robust security features that match or even surpass those of on-premise solutions.
-
Myth: It Is Only for Small Businesses:
Reality: It is suitable for businesses of all sizes, from startups to large enterprises. In fact, many enterprises leverage software-as-a-service to streamline operations, reduce IT complexity, and stay agile in a rapidly changing business landscape.
-
Myth: Software-As-A-Service Applications Lack Customization:
Reality: While these applications are standardized to cater to a broader user base, many providers offer customization options. Businesses can often configure settings, integrate with other tools, and adapt workflows to align the software with their specific needs.
-
Myth: Applications Always Have Hidden Costs:
Reality: While subscriptions involve ongoing costs, they typically include maintenance, updates, and support. Compared to on-premise solutions, where hidden costs like hardware upgrades and maintenance can accumulate, It provides greater transparency and predictability in total costs.
-
Myth: You Lose Control Over Your Data:
Reality: Software service providers prioritize data security and compliance. While data is stored off-site, reputable providers implement strict access controls, encryption, and adhere to data protection regulations. Businesses retain ownership of their data and can access, export, and delete it as needed.
What Future Holds For SaaS Application?
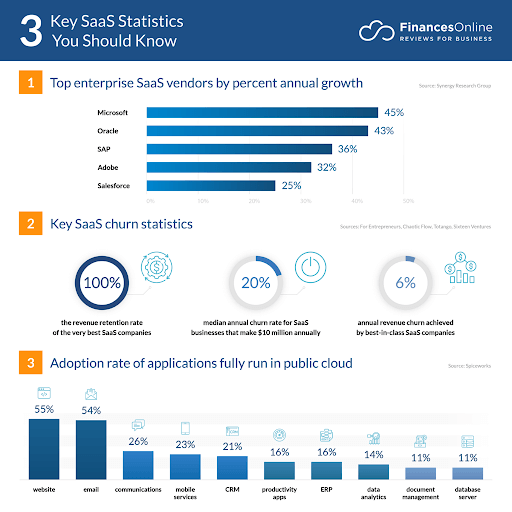
(Image source: https://financesonline.com/)
- SaaS is a cloud-based application platform; according to statistics the global market for cloud related software services will surpass $520 Billion in 2023.
- According to a recent study, nearly 1/3rd of the companies invested in cloud computing.
- In the year 2022 the hybrid cloud market was $54.34 Billion which is expected to reach $ 201 Billion in 2032.
- Nearly 90% of the active companies around the world have adopted cloud technology.
- Amazon cloud service or AWS is the leading SaaS solution provider. It owns 32% of shares around the world.
Conclusion
Software-as-a-Service has revolutionized the way enterprises approach software adoption and usage.
Its accessibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency make it the best option for modern enterprise businesses.
By harnessing the power of SaaS, enterprises can drive innovation, enhance collaboration, and stay agile in an ever-changing business landscape.
FAQs
Q1 – Who Owns SaaS Product Data?
Answer – The ownership of data in a SaaS product typically rests with the customer or the organization that subscribes to the service. Software service providers act as custodians of the data and are responsible for its storage and security. It’s important to review the terms of service and data usage policies provided by the vendor to understand the specifics of data ownership and usage rights.
Q2 – What If My Software-As-a-Service Provider Goes Out Of Business?
Answer – If your software service provider goes out of business, it can create challenges for your organization. It’s crucial to have a contingency plan in place. Ideally, before subscribing to their service, ensure that the contract includes provisions for data retrieval and transition in case the vendor becomes non-operational. Backup your data regularly and maintain awareness of the financial stability and reputation of the software-as-a-service developers.
Q3 – Can Applications be Customized to Fit Enterprise-Specific Needs?
Answer – Yes, many software service applications offer customization options. While these solutions are standardized to cater to a broad audience, they often provide configuration settings, integration capabilities, and extensions that allow businesses to adapt the software to their specific needs. However, the extent of customization may vary depending on the provider and the nature of the application.
Q4 – Is It Secure For Enterprise-Level Data?
Answer – Reputable software service providers prioritize data security and invest in robust measures to protect enterprise-level data. These measures can include encryption, access controls, regular security audits, compliance with industry regulations, and data backup strategies. While security concerns are valid, many applications provide a high level of security that can often match or surpass on-premise solutions, provided you choose a reliable and trusted vendor.






