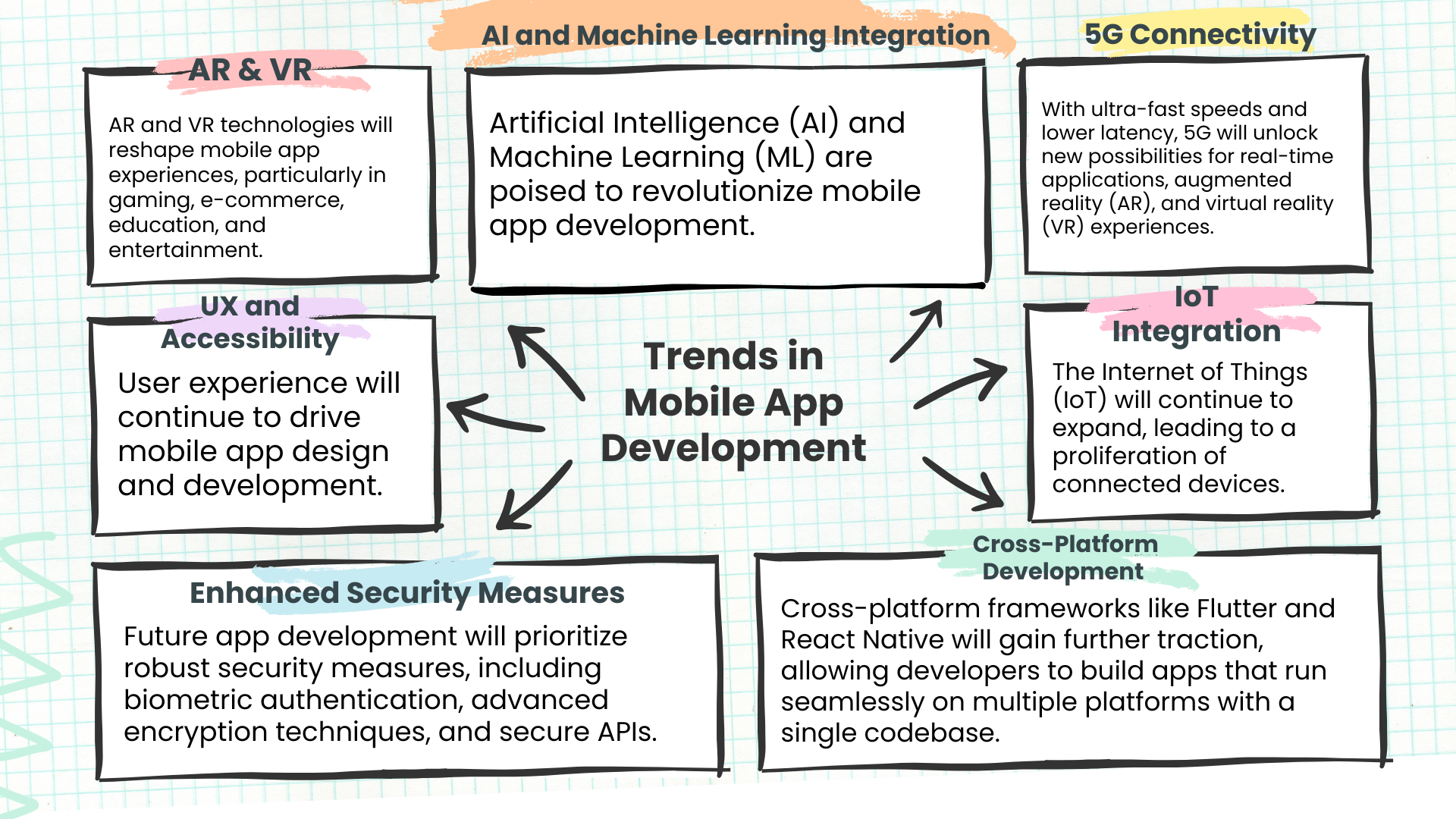
Mobile presence is a must-have tool for businesses to succeed in today’s market. It is an integral part of today’s web presence. Be it for building a new application for your startup or scaling an existing app, your business needs app scalability for long-term success.
As your use base grows you need to scale your app to accommodate the new users. If your app is not designed for scalability your application will face various performance and security issues which will impact your user experience.
To ensure that your latest mobile app development handles the increased number of users, requests, and data we will explore the principles and best practices for building scalable mobile apps that can stand the test of time.
What is Scalability in Mobile App Development?
Scalability is the ability of the app to handle an increasing number of users, requests, and data while at the same time maintaining performance and functionality.
A scalable mobile app development is designed to grow seamlessly along with the growing business. It can easily scale up in complexity and traffic without compromising its speed, reliability, and user experience.
In simple terms, scalability suggests that the applications’ user base and features expand so that the infrastructure can handle the increased load without slowing down the performance.
Scalability is not just about adding more resources, it’s about facilitating your app to perform efficiently and effectively as your business and user needs evolve.
Key Principles of Building Scalable Mobile Apps
1. Modular Architecture
The first thing to do to ensure a scalable mobile app is to build the app in modular architecture. This modular approach involves breaking down the app into smaller and more independent components. In this process, each model can be developed independently and when integrated together the complete app works as a single entity.
This process also ensures that you can scale up or down the application easily simply by adding or reducing the module in the app. For example, If the payment system becomes more complex, you can scale it independently without affecting the rest of the application.
When developing the backend of the application you should use microservices where each service is responsible for the specific task and it can be scaled independently.
2. Optimize Performance Early On
Performance optimization is another important aspect of the mobile app development process. To achieve a high-performance mobile app you need to focus on both frontend and backend efficiency. You should also ensure that the app user interface is responsive and loads faster even with limited resources.
Backend development best practices include optimizing database queries, caching data, and reducing server load. You should optimize your images, videos, and other media files to reduce the size. You should also consider implementing lazy loading and minimizing network requests by implementing data transfer protocols such as HTTPS.
3. Cloud Infrastructure and Scalability
Implement cloud platforms such as Amazon Web Services(AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud for cost-effective solutions. This way you scale resources on-demand which can ensure that your app handles traffic spikes without downgrading performance.
Choose a cloud service that enables your application resources to efficiently distribute the traffic and access multiple servers. They can also provide tools for monitoring, analytics, and automated scaling.
You must choose a cloud solution with auto-scaling features and leverage content delivery networks to reduce latency for users.
4. Use a Robust Database System
Along with your mobile app, the amount of data you need to manage also increases. Using the right database is essential for ensuring that your application can scale effectively.
The database should be capable of handling large amounts of data and delivering fast read and write operations even when your user base expands.
There are two primary types of databases:
- Relational (SQL)
- Non-Relational (NoSQL)
- SQL databases are perfect for structured data with relationships
- NoSQL databases excel at handling large volumes of unstructured data
When you choose a database you should consider your application’s data requirements such as how much data it needs to store how often data can change and how you will query it.
Best Practice:
- When you have an app with structured data and complex queries you should use a SQL database such as PostgreSQL and MySQL.
- When you have applications with large amounts of unstructured and semi-structured data you should use a NoSQL database such as MongoDB and Cassandra.
- You should implement database sharding i.e. to split data across multiple databases, this will improve performance and scalability.
5. Implement Caching Mechanisms
Caching is a powerful technique to improve the performance and scalability of the application. By storing these data in memory, you can reduce the load on the server and database which enables the app to serve content faster.
It also helps you minimize the need for repeated requests and improves the overall user experience.
There are multiple styles of caching mechanisms that you can implement including server-side caching, client-side caching, and reverse proxy caching.
Choosing the right types of caching depends on the application’s architecture and data access patterns.
Best Practice:
- Use in-memory caching systems such as Redis or Mem-cached for fast access to frequently requested data.
- You can also cache static content such as images and JSON responses. On the client side, you can use the technologies such as service workers and local storage.
- You can set the right expiration times for cached data in order to ensure that the users get the most up-to-date information.
6. Asynchronous and Background Processing
Handle long-running tasks and processes, as it is essential for maintaining a responsive and scalable mobile app.
If your app needs features that involve data processing, notifications, and 3rd-party integrations, it is essential for the app to be able to process these tasks in the background so that they don’t block the main thread or user interactions.
Asynchronous processing can enable your app to continue functioning normally, even when handling resource-intensive tasks. You can process user requests in the background and notify users once the task is completed.
Best Practice:
- Enable message queues like RabbitMQ or Apache Kafka to handle background tasks.
- For mobile applications, you can utilize background processing frameworks such as Firebase Cloud Functions and Native background services for iOS and Android.
7. Plan for Load Balancing and Redundancy
Ensure that your app traffic is evenly distributed. Load balancing is one such feature that lets your application scale up where traffic is evenly distributed across multiple servers. This can prevent any single server from becoming overwhelmed. Redundancy is also important for ensuring high availability.
The best practices include integrating services like AWS Elastic Load Balancer and Nginx. You should also implement database replication and backup strategies which will ensure that the data you implement is safe across multiple servers and locations.
8. Prioritize Security at Scale
When it comes to mobile app scalability, security is the primary concern. When the application grows it brings in a ton of users as well. This also makes your app attractive to cyberattacks. Implement authentication, encryption, and authorization mechanisms to secure app data and user interactions.
Use authentication such as OAuth, two-factor authentication, and single sign-on. Also, encrypt data using protocols such as HTTPS and AES.
Best Practices for Scaling Mobile Apps Effectively
- Plan for Future Growth
Plan by choosing scalable technologies and tools from the beginning. You should keep the app’s long-term vision and choose a platform that can accommodate future growth.
- Use Analytics and Monitoring Tools
Monitoring the application’s performance and user behavior is important for identifying the bottlenecks, errors, and areas for improvement. You can use tools such as Google Analytics, Firebase Analytics, and New Relic to help you track key metrics and respond proactively.
- Build for Offline Capabilities
You need users who will have a reliable internet connection. Ensure a smooth experience by implementing offline capabilities such as local data storage, caching, and sync functionalities.
- Test at Scale
Before you launch the application you should test its performance under high load to ensure that it can take on the traffic spikes. Implement tools such as LoadRunner, Apache JMeter, or BlazeMeter to simulate heavy traffic and identify potential issues.
- Consider Cross-Platform Development
Support both iOS and Android, by using cross-platform frameworks such as Flutter, React Native, and Xamarin.
These frameworks enable you to write most of your code once and deploy it on both platforms which saves time and resources while maintaining scalability.
Conclusion
Building a scalable mobile app requires careful planning, and for that, you need the right technology stack for which you need to adhere to its best practices.
Following principles such as modular architecture, optimizing performance, and using cloud infrastructure can leverage caching. You can ensure that the app will handle increasing traffic, data, and user demands.
Security, load balancing, and background processing are essential for building an app that is reliable and efficient to grow.
Security, load balancing, and background processing are also essential to building an app that remains reliable and efficient as it grows. Scalability is about future-proofing your mobile app.
When you build the application with scalability in mind, you can ensure that the app can evolve alongside the business. This provides a seamless experience for users and meets the demands of the market.