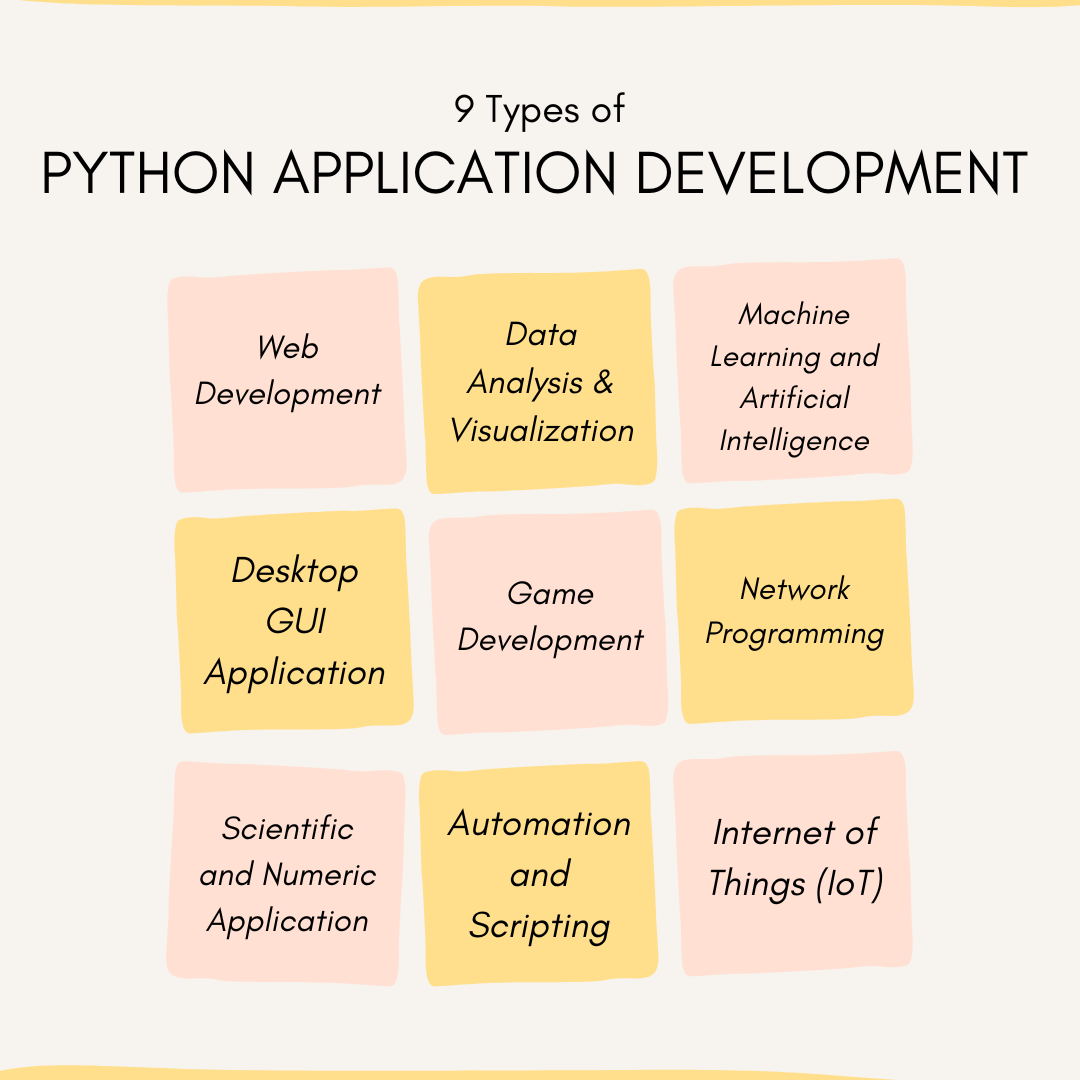
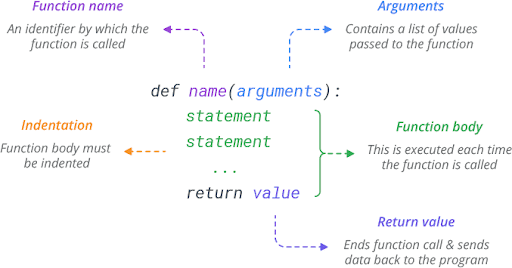
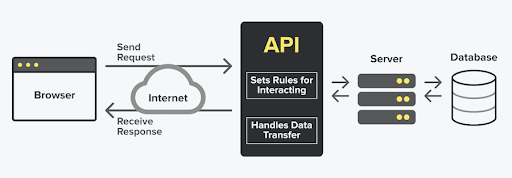
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are the fastest developing technology in the field of computer programming.
Companies like Facebook, Tesla and Google are spending millions to develop AI tools that can solve real world problems.
A most recent example of such development is ChatGPT which has taken the world by storm.
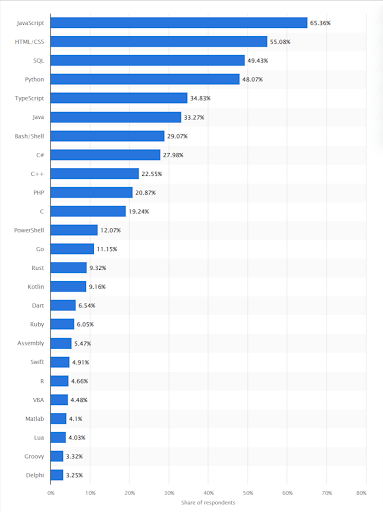
When it comes to AI app development there are various programming languages to choose from such as JavaScript, Java, Scala, Julia, C++ and Python.
Among all these languages Python is the most suitable and sought-after programming language.
Its simplicity, extensive libraries, and thriving community have made it the preferred choice for AI and ML development.
In this blog, we’ll delve into the compelling reasons why Python stands out as the best programming language for AI and ML.
-
Ease of Learning and Readability
Python features a clean and concise syntax which makes it easier to learn and understand. Its code readability resembles verbal English which makes it accessible to both beginners and seasoned developers.
This simplicity of the Python programming language makes it crucial in AI and ML application development as it requires fast adoption.
-
Vast Ecosystem of Libraries and Frameworks
Python app development is popular because of a wide collection of libraries and frameworks. These libraries act as modules which include pre-written code which can simply be published to add a feature to the code.
AI and ML application development requires continuous data processing and these libraries enable developers to access, handle and transform data.
Libraries like TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn, and Keras simplify complex tasks like neural network implementation, data preprocessing, and model evaluation.
Explained below are top 5 such libraries used for AI development:
Scikit-learn is a versatile library for ML in Python. It provides simple and efficient tools for data mining and data analysis.
Scikit-learn offers a wide range of algorithms for classification, regression, clustering, dimensionality reduction, and more.
It’s known for its user-friendly API and is suitable for both beginners and experts in ML.
Example: Building a simple machine learning model to classify iris flowers
1st – from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris.data, iris.target, test_size=0.3)
model = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
predictions = model.predict(X_test)
TensorFlow is an open-source deep learning framework developed by Google.
It excels in building and training neural networks for tasks like image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and more.
TensorFlow offers flexibility for research and production-grade ML model deployment. Its high-level API, Keras, makes it accessible for beginners.
Example: Creating a basic neural network for image classification
import tensorflow as tf
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation=’relu’),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.2),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation=’softmax’)
])
model.compile(optimizer=’adam’,
loss=’sparse_categorical_crossentropy’,
metrics=[‘accuracy’])
model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5)
PyTorch is another popular deep learning framework known for its dynamic computation graph, which enables more intuitive and flexible model building.
PyTorch is widely adopted in research due to its ease of debugging and prototyping.
It’s often the choice for those who prefer a more “Pythonic” approach to deep learning.
Example: Building a simple convolutional neural network (CNN) for image classification
1st – import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, 3)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(32*26*26, 64)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(64, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = x.view(-1, 32*26*26)
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
return x
net = Net()
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
-
NLTK (Natural Language Toolkit):
NLTK is a comprehensive library for natural language processing (NLP) in Python.
It provides tools for text tokenization, stemming, parsing, and sentiment analysis, among others.
NLTK is widely used in text mining, chatbot development, and linguistic research.
Example: Performing text tokenization and sentiment analysis
import nltk
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk.sentiment.vader import SentimentIntensityAnalyzer
nltk.download(‘punkt’)
nltk.download(‘vader_lexicon’)
text = “Python is a versatile programming language. I love using it!”
tokens = word_tokenize(text)
sia = SentimentIntensityAnalyzer()
sentiment_scores = sia.polarity_scores(text)
OpenCV (Open Source Computer Vision Library):
OpenCV is a powerful library for computer vision and image processing tasks.
It offers a wide range of functionalities, including image and video analysis, object detection, facial recognition, and more.
OpenCV is essential for applications like image manipulation, autonomous vehicles, and surveillance systems.
Example: Performing image processing and face detection
import cv2 image = cv2.imread(‘image.jpg’) gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier(‘haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml’) faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, scaleFactor=1.3, minNeighbors=5)
-
Active and Supportive Community
Developers, data scientists, and researchers worldwide contribute to forums, blogs, and open-source projects, providing invaluable support and resources to fellow enthusiasts.
Developers choose programming technologies that have a strong community support. In this scenario, Python is a suitable programming language because it’s an open source technology and provides resources for programmers of all levels of proficiency.
A significant amount of Python documentation which is available online as well as in community forums programmers discuss error solving, bug fixing and code improvement to help programmers become better at Python programming.
Python programming language is absolutely free and provides a wide range of useful libraries and tools.
-
Cross-Platform Compatibility
Python’s cross-platform compatibility is a standout feature which makes it a versatile and widely adopted programming language.
Whether you are using Windows, MacOS, or Linux you can write the Python code once and run on multiple platforms seamlessly without making a major modification.
This is a must-have feature for developers as well as Python development companies as it ensures a consistent behavior and functionality across various operating systems.
This reduces the compatibility issues which are inherent in other programming languages. Python cross-platform compatibility makes it a suitable choice for building applications and software that needs to reach a broad user base.
This enables developers to focus on their code’s functionality rather than worrying about system-specific nuances. Python runs seamlessly on major operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
This versatility ensures that AI and ML projects can be developed and deployed across different platforms without major compatibility issues.
-
Scalability
Python’s scalability is one of the most important features that contributes to its widespread adoption in domains such as web development, data science, and artificial intelligence.
This versatility of Python programming languages enables seamless accommodation of projects of varying sizes and complexities. Python can be employed by both beginners and experienced developers for enterprise application development.
Python offers the flexibility to scale up and down when needed. This robust ecosystem of libraries, frameworks, tools along with the rocksolid community support makes it one of the most sought-after programming languages for AI and ML development.
Python’s scalability ensures that it can adapt to the evolving needs of developers and organizations, making it a reliable choice for a wide spectrum of applications.
-
Integration Capabilities
Python’s wide integration capabilities makes it a versatile programming language. It seamlessly integrated with other languages such as C, C++, and Java thereby enabling developers to leverage the various libraries and the existing codes.
This interoperability is particularly advantageous when working on projects that require the performance optimization.
Python’s support for web services, APIs, and data exchange formats like JSON and XML further enhances its integration capabilities, enabling smooth communication with web-based applications and data sources.
This flexibility in integration not only saves development time but also allows Python to be a valuable component in a wide range of software ecosystems and industries, from web development to Artificial intelligence and beyond.
-
Data Handling and Analysis
Python’s data handling capabilities makes it the most popular programming language for data scientists and analysts. It offers powerful libraries and tools for data manipulation, analysis and visualisation.
Libraries like NumPy and pandas provide efficient data structures and functions for handling structured data, making tasks like filtering, sorting, and aggregating data a breeze.
Python’s native support for dictionaries and lists simplifies unstructured data handling. Additionally, libraries like Matplotlib, Seaborn, and Plotly enable data visualization, allowing users to create informative charts and plots.
Python excels in data manipulation and analysis, making it an ideal choice for AI and ML, which heavily rely on data processing.
-
Visualization Tools
Python’s visualization tools have their application in data science and analysis. It provides an array of libraries such as Matplotlib, Seaborn, Plotly and Bokeh which empower data professionals to create compelling and insightful visualizations.
Whether it is for crafting interactive charts or plotting complex data, Python’s visualization capabilities are diverse and adaptable.
These tools not only enable data exploration but also assist in communicating various findings effectively to both technical and non-technical stakeholder.
The Python community continually enriches these libraries, ensuring they remain at the forefront of data visualization innovations.
Whether you’re working on data analysis, machine learning, or any data-centric task, Python’s visualization tools provide the visual narrative needed to extract meaning and make informed decisions from data.
-
Flexibility and Prototyping
Python is well-known for its flexibility and rapid development capabilities which makes it an excellent choice for prototyping.
This prototyping involves creation of preliminary versions of software or applications to test concepts, design ideas, and functionality before moving to full-scale development.
Python features dynamic typing, concise syntax and extensive libraries which allow Python developers to quickly transform ideas into working prototypes.
With Python, developers can focus more on the logic and functionality of their prototypes rather than getting bogged down by complex syntax.
This facilitates a streamlined development process which enables rapid interactions and easy modification thereby making Python the most preferred language for AI and ML algorithms, web application and other software prototypes.
Be it for creating novel AI models or building proof-of-concept applications, Python prototyping features can empower developers to efficiently bring ideas to life and gather valuable insights for development.
-
Open Source and Free
Python is not only a powerful and versatile programming language but also stands out for its accessibility. One of its most compelling attributes is its open-source and free nature.
Python’s open-source status means that it’s available to anyone for use, modification, and distribution without any licensing fees. This fosters a vibrant and collaborative community of developers, data scientists, and enthusiasts who contribute to its growth and improvement.
Whether you’re a beginner exploring programming for the first time or a seasoned developer working on complex AI or web applications, Python’s open-source nature ensures that you have access to a wealth of resources and support.
And making it an ideal choice for a wide range of projects and industries.
What are The Top 10 Trends in AI and ML
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are dynamic fields that constantly evolve.
-
Explainable AI (XAI):
XAI is gaining importance as AI systems become more complex. It focuses on making AI algorithms more transparent and interpretable, allowing humans to understand how AI decisions are made, which is crucial for applications like healthcare and finance.
-
Federated Learning:
Federated Learning is a privacy-focused approach where machine learning models are trained across decentralized devices or servers holding local data. It enables collaborative model training without sharing raw data, addressing privacy concerns.
-
AI in Healthcare:
AI is revolutionizing healthcare with applications in medical imaging, drug discovery, personalized medicine, and patient care. AI-driven diagnostics and treatment recommendations are becoming more accurate and accessible.
-
AI in Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP is advancing rapidly, with models like GPT-3 and BERT setting new benchmarks. AI-powered language models are used in chatbots, language translation, content generation, and more.
-
AI in Edge Computing:
AI is moving closer to the data source with edge computing. This trend enables real-time AI processing on devices like smartphones, IoT sensors, and autonomous vehicles, reducing latency and enhancing privacy.
-
AI Ethics and Bias Mitigation:
As AI systems impact society, ethical considerations are paramount. Addressing bias, fairness, and ethical AI development practices are becoming crucial areas of focus.
-
AI in Cybersecurity:
AI-driven cyber-security solutions are more effective at identifying and mitigating cyber threats. They analyze vast amounts of data to detect anomalies and respond to attacks in real-time.
-
AI in Autonomous Systems:
AI is powering autonomous vehicles, drones, and robots. These systems are becoming increasingly capable of making complex decisions in dynamic environments, enhancing safety and efficiency.
-
AI in Finance:
AI is transforming the financial sector through algorithmic trading, fraud detection, risk assessment, and customer service chat-bots. It’s also driving innovations in blockchain and cryptocurrencies.
-
AI for Climate and Sustainability:
AI is being applied to address climate change and sustainability challenges. It’s used in climate modeling, energy optimization, and conservation efforts to make a positive impact on the environment.
Top Things to Consider When Choosing Python Developers for AI and ML Development
Hiring Python developers for AI and ML app development is a critical task that requires careful consideration.
Here are the top five things to keep in mind when making your hiring decisions:
-
Skillset and Experience:
Look for candidates with a strong foundation in Python programming, as well as expertise in AI and ML frameworks and libraries such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn, and Keras.
They should have a proven track record of working on AI and ML projects, preferably in roles where they’ve implemented machine learning algorithms, deep learning models, and data pre-processing pipelines.
-
Domain Knowledge:
Depending on your specific AI and ML application, consider candidates with domain knowledge relevant to your industry.
Whether it’s healthcare, finance, e-commerce, or any other field, having an understanding of the domain can be invaluable when designing and implementing AI solutions.
-
Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking:
AI and ML app development often involves tackling complex problems. Assess candidates for their problem-solving abilities, critical thinking skills, and their capacity to adapt to new challenges. Ask them to solve real-world AI and ML problems during interviews to evaluate their problem-solving skills.
-
Communication and Collaboration:
Effective communication is crucial in a development team. Ensure that candidates can explain complex AI and ML concepts in a clear and understandable manner.
Evaluate their ability to collaborate with cross-functional teams, including data scientists, designers, and product managers, as teamwork is essential for successful AI and ML projects.
-
Portfolio and Projects:
Review candidates’ portfolios and ask for examples of their previous AI and ML projects. A strong portfolio demonstrates their practical experience and the ability to deliver tangible results.
Additionally, consider their contributions to open-source AI and ML projects, which can be a sign of their commitment to the field.
Conclusion
Python’s supremacy in AI and ML development is not accidental. Its combination of simplicity, powerful libraries, and a supportive community makes it the best programming language for tackling complex AI and ML projects.
These factors also make it one of the most sought-after programming languages for Python application development as well as AI and ML application development.
Top AI app development companies in the world use Python to create interactive AI apps.
Whether you’re a beginner looking to enter the field or an experienced practitioner pushing the boundaries of what’s possible, Python offers the tools and resources needed to excel in the exciting world of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
Embrace Python, and you’ll find yourself at the forefront of innovation in this rapidly evolving field.